What is EDI? A Simple Guide to Electronic Data Interchange
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a digital method for exchanging business documents between companies — like suppliers, retailers, manufacturers, and logistics providers.
Instead of sending paper documents or manually entering data, EDI lets businesses automate and streamline communication by sending standardized files directly between computer systems.
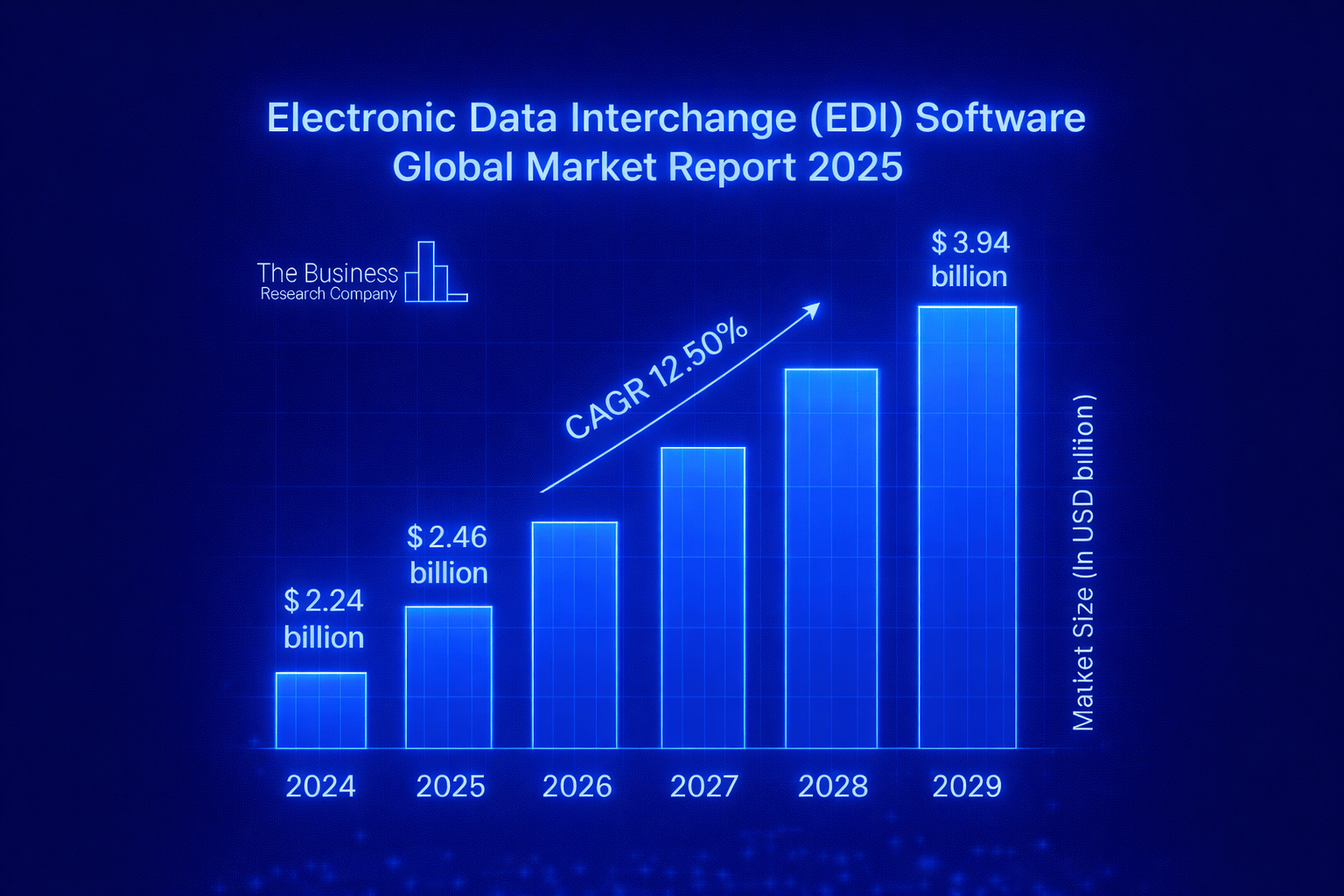
The provided text states that the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) software market is projected to reach $2.46 billion in 2025. This represents a 9.5% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from its 2024 size of $2.24 billion.
How EDI Works
EDI software uses standard formats to send documents like:
In North America, most EDI systems follow the ANSI X12 standard. In Europe and globally, the EDIFACT standard is often used.
Purchase Orders (PO)

Invoices

Advance Shipping Notices (ASN)

Payment confirmations
EDI = Smarter, Faster Business
By replacing emails, faxes, and paperwork with automated data exchange, EDI helps your business run smoother and scale faster. It’s a key tool for companies that want to stay competitive and efficient in today’s fast-moving digital economy.
The 4 Key Components of a Modern EDI System
A fully functional EDI system consists of essential components that automate the exchange of business documents between your system and trading partners. These elements work together to ensure seamless, secure, and accurate EDI integration.
All components are delivered through a fully managed EDI solution, helping businesses stay compliant and efficient.
The EDI translator converts business documents from your internal format into standard EDI formats (like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT), and vice versa. This ensures that every document meets the technical requirements of each trading partner, regardless of the systems they use.
2. EDI Mapping Tables
EDI mapping defines how data flows between your ERP or business system and your partners’ platforms. These mapping rules guide the EDI translator, ensuring that each data point is correctly placed — so your purchase orders, invoices, and shipping documents are always accurate.
3. Secure EDI Network
A secure EDI communication network allows you to transmit documents quickly and safely. With end-to-end encryption and real-time traceability, you can exchange sensitive business data with confidence and stay aligned with industry compliance standards.
4. Managed EDI Support & Maintenance
As EDI standards and trading partner requirements evolve, your system needs to keep up. A managed EDI provider offers proactive updates, monitoring, and 24/7 support — helping your business remain compliant and minimizing downtime.
How Does EDI Work?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) replaces traditional communication methods—like mail, fax, or email—with automated, system-to-system document exchange. No matter what software or platform two businesses use, EDI integration ensures data is shared in a standardized and structured format.
Here's How the EDI Process Works:
Business Document Creation

Your internal system (ERP, WMS, or accounting software) generates a business document, such as a Purchase Order (PO), Invoice, or Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN).
EDI Document Preparation

The generated document is passed to your EDI software or middleware, where it's prepped with necessary metadata, partner identification, and business rules before translation.
EDI Format Conversion

The document is converted into a standardized EDI format (e.g., 850 for PO, 810 for Invoice) using predefined schemas, making it understandable by both sender and receiver systems.
Secure Data Transmission
The translated EDI file is transmitted securely using a protocol like AS2, VAN, SFTP, or API—ensuring reliable and encrypted delivery to your trading partner.
Inbound EDI Mapping & Integration

The receiving partner's EDI system accepts the file and maps the EDI data into their internal system format (e.g., ERP or WMS), enabling seamless, automated ingestion.
Automated Business Workflows

Once integrated, the document triggers internal workflows like order processing, inventory updates, invoice generation, or shipping—removing manual effort and delays.
Certainly! Here’s a rephrased, SEO-friendly version of your content for website use, keeping it simple, clear, and optimized for keywords like EDI mapping, EDI solutions, integrated EDI, and more:
What Does EDI Mean for Your Business?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a powerful business tool that automates the exchange of documents—such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices—directly between computer systems.
Instead of relying on emails, faxes, or manual data entry, EDI integration standardizes and streamlines communication with your suppliers, distributors, and customers.
With EDI: Automated, Fast, and Reliable
EDI automates the entire process. Your system sends a purchase order directly to your trading partner’s ERP. The document is processed instantly, and the invoice is returned in real time—no human intervention needed.
✅ Fewer errors
✅ Faster order cycles
✅ Stronger trading partner relationships
✅ Scalable, efficient supply chain operations
Without EDI: Manual, Slow, and Risky
When you send a purchase order by email or fax, the supplier has to manually enter it into their system. This slows down the process and increases the risk of:
❌ Data entry errors
❌ Lost documents
❌ Delayed order fulfillment
❌ Communication breakdowns
Why EDI Matters for Modern Businesses
In today’s fast-paced, digital economy, automation is key to growth and efficiency. With EDI:
- Orders and invoices are processed 24/7, even outside business hours
- Standardized formats ensure accuracy and compliance
- Your business can scale without adding manual workload
Whether you're in retail, manufacturing, distribution, or logistics, implementing EDI means faster operations, fewer mistakes, and a more competitive edge.
Common Business Processes Powered by EDI
EDI is used across a wide range of business operations to automate and streamline document exchange. Some of the most common processes include:
- Purchase Orders (POs)
- Invoices and Payment Remittance
- Advance Shipping Notices (ASNs) and Manifests
- Purchase Order Acknowledgements
- Warehouse Shipping Orders
Want to explore more?
View the complete list of EDI transaction codes
EDI 832 - Price/Sales Catalog
EDI 846 - Inventory Inquiry
EDI 850 - Purchase Order
EDI 997 - Functional Acknowledgement
EDI 860 - Update Purchase Order
EDI 855 - Purchase Acknowledgement
EDI 810 - Invoice
EDI for Warehouse Operations – Orders, Transfers & Receipts